When you embark on the family history research journey, it’s crucial to understand that national borders and political entities are not static; they change over time. A classic example of this fluidity is the relationship between Prussia and Germany.
In today’s geopolitical landscape, Germany is a well-defined nation-state, but once a dominant European power, Prussia no longer exists as a separate country or state. Read on as we explore the intricate differences between Prussia and Germany and elucidate why understanding these distinctions is vital if your family history research touches these regions.
Table of Contents
- Prussia Vs. Germany: A Tale Of Two Entities And Their Historical Interplay
- Germany – A Confederation Of States
- Countries Today Making Up Former Prussian Territories
- Countries That Contributed To Modern Germany
- Historical Differences
- Why All This Matters For Family History Research
- Related Questions
Prussia Vs. Germany: A Tale Of Two Entities And Their Historical Interplay
The subject of Prussia and Germany often gets intertwined, leading to historical and geographical confusion. We aim to untangle this web by comparing and contrasting the historical evolution of Prussia and Germany while highlighting their defining characteristics.
Understanding these differences and similarities is essential, particularly when digging into family history across these geographical and political entities.
What Is Prussia?
Prussia was a historical German state that originated in the early 16th century as the Duchy of Prussia. It was initially a part of the Teutonic Order and later evolved into the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701.

Prussia was one of the most influential states in Europe, known for its military prowess, disciplined administration, and role in shaping modern Germany. Its capital was originally Königsberg (now Kaliningrad, Russia), and later moved to Berlin.
What Is Germany?
In contrast, Germany is a modern nation-state in the heart of Europe, bordered by nine countries, including Denmark, Poland, the Czech Republic, Austria, Switzerland, France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands.

As we know it today, Germany was officially unified on January 18, 1871, although the roots of Germanic peoples and states go back much further.
Germany – A Confederation Of States
Before becoming a unified nation, the territory known today as Germany was home to many states, varying from free cities to grand duchies and kingdoms. This collection of territories was loosely organized into the Holy Roman Empire, which existed from 962 until its dissolution in 1806.
After the fall of the Holy Roman Empire, the German Confederation emerged in 1815, followed by the North German Confederation in 1867, both of which served as precursors to the German Empire in 1871.
The Formation Of Modern Germany
As a unified nation, Germany came into being through a series of wars led primarily by Prussia under the guidance of Otto von Bismarck. These included the Second Schleswig War (1864), the Austro-Prussian War (1866), and the Franco-Prussian War (1870-71).
After defeating France, the German states unified into the German Empire, with King Wilhelm I of Prussia becoming the German Emperor (Kaiser) and Berlin becoming the capital.
This marked the decline of Prussia as an independent entity, as it was fully incorporated into the German Empire.
Countries Today Making Up Former Prussian Territories
Modern Prussia no longer exists as a political entity, but its former territories are now part of modern Germany, Poland, Russia, and Lithuania. Kaliningrad, once Königsberg, is a Russian exclave.
Many regions in eastern Germany and western Poland were also once integral parts of Prussia.
Countries That Contributed To Modern Germany
Modern Germany was formed from numerous states, including but not limited to Prussia, Bavaria, Saxony, Hanover, Württemberg, Baden, and Hesse. These states were individual entities with their laws, currencies, and traditions before unification.
Historical Differences
There exist distinct historical disparities between Prussia and Germany that are worth exploring. Continue reading as we delve into some of these fascinating differences.
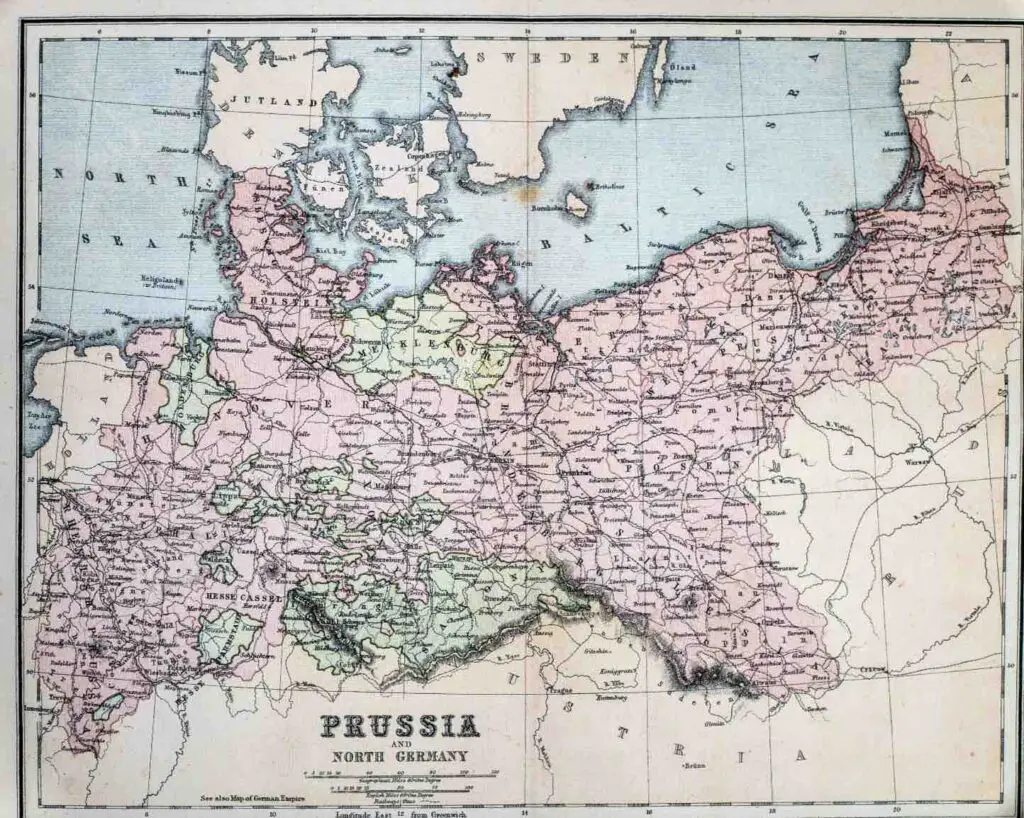
Prussia
Here are some of the significant attributes of Prussia and what this means for Prussia.
- Military Influence: Prussia was a military state. The Prussian Army was one of the most formidable in Europe, and the aggressive culture influenced many aspects of daily life.
- Absolutism and Administration: Prussia was known for its bureaucratic efficiency and centralized power. The notion of ‘Prussian Virtues’ such as discipline, punctuality, and duty were instilled in society.
- Religion: While Germany had a mix of Catholic and Protestant states, Prussia was primarily Protestant.
Germany
Here are some historical aspects of Germany and why it is essential.
- Cultural Diversity: Unlike Prussia, which had a relatively homogeneous culture, Germany is a blend of various regional cultures.
- Economic Strength: Modern Germany is known for its economic prowess, particularly in engineering, automobiles, and technology.
- Democratic Principles: Post-WWII, Germany was a democratic state, contrasting sharply with the autocratic governance that characterized Prussia.
Why All This Matters For Family History Research
When researching your family history, especially if you are researching German or Prussian ancestors, it is crucial to understand these nuances for several reasons:
- Migration Patterns: Knowing the historical timeline can help you track family migrations, especially during political upheaval or territorial changes.
- Religious Affiliations: Different regions had different predominant religions, which might be relevant when searching through religious records.
- Name Changes: Place names may have changed over time, especially in areas that have shifted from one state to another or between countries.
- Legal Documents: The legal systems vary from state to state, affecting where you might find birth, marriage, or death certificates.
Understanding the difference between Prussia and Germany is not just a matter of historical interest but also a practical concern for anyone delving into their family history.
The formation of these entities has seen shifts in borders, governance systems, and even cultures. A keen understanding of these shifts is essential for accurately tracing one’s lineage and grasping the milieu in which ancestors lived.
With this knowledge, you are better prepared to explore your roots in this rich and complex landscape.
The Hummel Family is a website all about Family History research. We focus on Swedish, German, English, Scottish, and American Genealogy. We also discussed Asia and China, as we had ancestors who spent many years in China.
You are welcome to join us and become part of our community by signing up for our FREE newsletter, The Hummel Family; sign up by clicking here.
Check out our Youtube Channel, Family History Buzz, by clicking here.
Related Questions
Minden-Lübbecke, Germany History And Wehking History Explored
We will look into this region’s history and take a closer look at the history of the Hummel family and this area of Germany. By exploring the history of this region and our family history, we hope to gain a deeper appreciation of the culture and traditions passed down through the generations. Read on as we discover the rich history of Minden-Lübbecke and the Hummel family together!
You can read more about, Minden-Lübbecke, Germany’s History, And Wehking History Explored by clicking here.
German US – Immigration & History Of The City Of Erdmannhausen, Ludwigsburg, Germany
Johann Gottlieb Hummel, my great great-great-grandfather, was born in 1829 in Erdmannhausen, Ludwigsburg, Germany. In the 1850s, he migrated from Erdmannhausen in Germany to The United States; he arrived in the United States just in time to fight in the US Civil. War.
You can discover more about German US – Immigration & History Of The City Of Erdmannhausen, Ludwigsburg, Germany by clicking here.
What Is The History of Westphalia, Germany?
Westphalia’s history goes back to the times of the ancient Saxons. For a period of time, Westphalia was under the rule of Napoleon and the French. Later Westphalia became a state of Prussia until it officially became part of Germany in 1945.
You can learn more by reading A History of Westphalia, Germany by clicking here.

